Introduction:
Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, is not only known for its majestic size and colorful bands of clouds but also for its intriguing collection of moons. With a staggering number of 79 confirmed moons, Jupiter hosts a diverse and captivating menagerie of celestial bodies. In this article, we embark on a journey through the mesmerizing realm of Jupiter's moons, uncovering their unique characteristics, fascinating discoveries, and the potential they hold for unlocking the secrets of our solar system.
1. The Galilean Moons:
Image credit - Universe today.Among Jupiter's many moons, the Galilean moons are the most well-known and prominent. Discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610, these four large moons—Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto—continue to astound scientists with their captivating features.
a. Io:
Io, the innermost of the Galilean moons, is the most volcanically active body in our solar system. Its surface is adorned with over 400 active volcanoes, spewing sulfur-rich plumes that create a vibrant and ever-changing landscape. The extreme volcanic activity on Io is a result of tidal forces induced by Jupiter and its neighboring moons.
b. Europa:
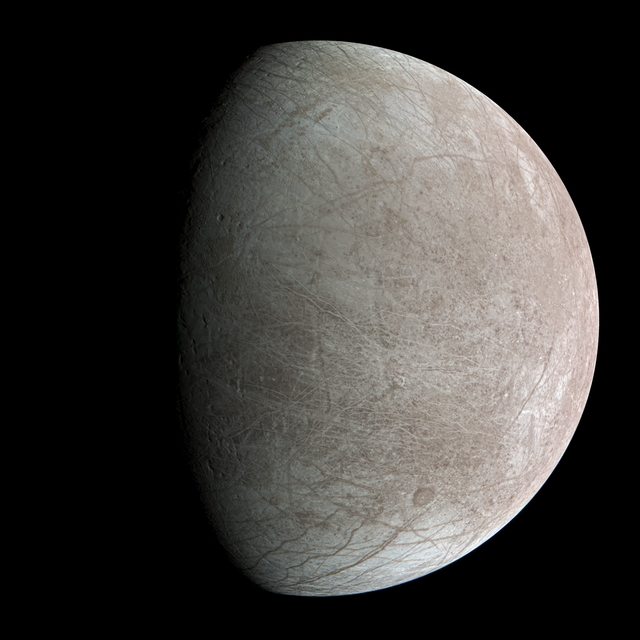
credit - wikipedia.Europa, often considered one of the most promising candidates for hosting extraterrestrial life, has an icy crust covering a global ocean of liquid water. This moon's surface exhibits a complex network of cracks and ridges, hinting at the possibility of subsurface water venting into space. Exploring Europa's hidden ocean may unveil valuable insights into the potential habitability of icy worlds beyond Earth.
c. Ganymede:
Ganymede, the largest moon in the solar system, surpasses even the planet Mercury in size. It possesses a magnetic field and a diverse geology, including a mix of ancient cratered regions, grooved terrain, and large dark regions known as "Galileo Regio." The presence of a subsurface ocean, sandwiched between layers of ice, further fuels scientific curiosity about this enigmatic moon.
d. Callisto:
Callisto, the outermost of the Galilean moons, is known for its heavily cratered surface, suggesting a lack of significant geological activity. It boasts an ancient and preserved landscape, making it a valuable celestial time capsule that offers insights into the early history of the solar system.
2. Beyond the Galilean Moons:
While the Galilean moons take center stage, Jupiter's moons extend far beyond this quartet. Many smaller moons, each with its distinct characteristics, orbit the gas giant.
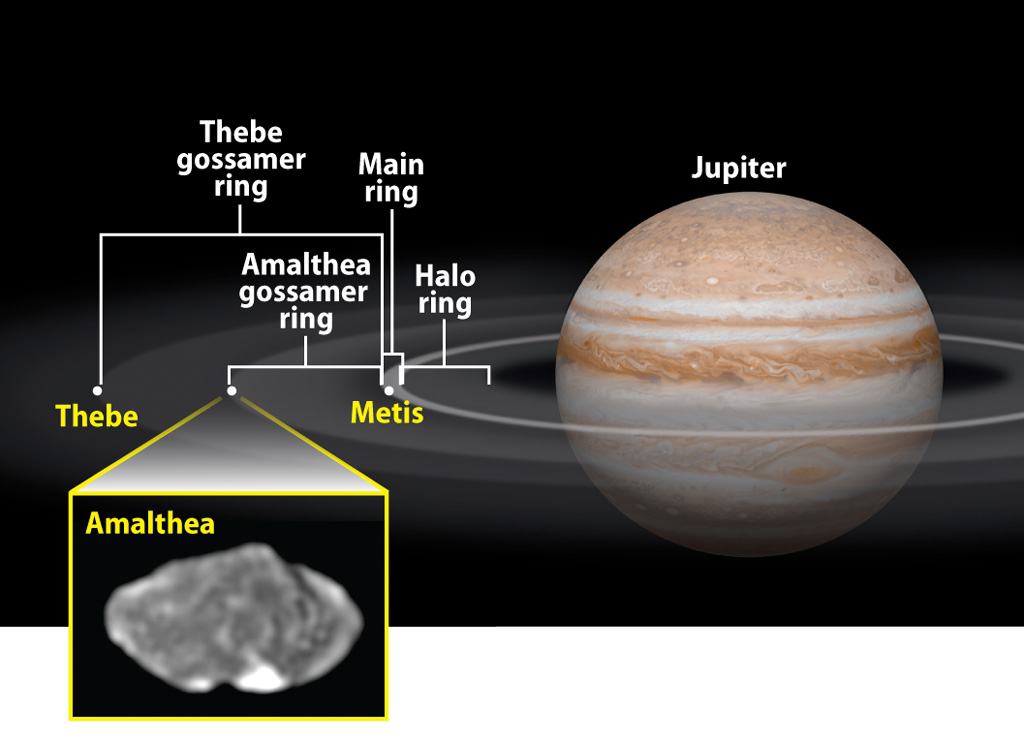
a. Amalthea:
credit - astronomy.comAmalthea, discovered in 1892, is the largest of Jupiter's inner moons. It is irregularly shaped and exhibits a reddish hue, possibly due to the presence of sulfur compounds on its surface. Understanding Amalthea's composition can provide valuable clues about the processes that shaped the inner regions of Jupiter's system.
b. Himalia Group:
This group comprises four moons—Himalia, Elara, Leda, and Lysithea—named after the lovers of Zeus in Greek mythology. They are irregularly shaped and likely captured asteroids or fragments of larger bodies. Exploring their origins and composition may contribute to our understanding of the early solar system.
c. The Outer Moons:
Beyond the Galilean moons lies a diverse collection of smaller moons, including Ananke, Carme, Pasiphae, and Sinope, among others. These moons orbit Jupiter in irregular paths and exhibit a wide range of colors, sizes, and surface features. They offer unique insights into the dynamics of Jupiter's outer regions and the complex interactions within the Jovian system.
3. Unveiling the Mysteries:
Jupiter's moons continue to captivate scientists and space enthusiasts alike, providing valuable opportunities for exploration and discovery. Future missions, such as NASA's Europa Clipper and the European Space Agency's JUICE (JUpiter ICy moons Explorer), aim to study Jupiter's moons in greater detail.
These missions will focus on investigating the potential habitability of Europa, examining Ganymede's magnetic field, and studying the composition and geology of other intriguing moons. By unraveling the mysteries of Jupiter's moons, scientists hope to gain insights into the formation of our solar system, the possibility of life beyond Earth, and the role of gas giants in shaping the cosmos.
Conclusion:
Jupiter's moons present an awe-inspiring panorama of diversity, revealing the splendor and complexity of our solar system. From the volcanic landscapes of Io to the hidden oceans of Europa and the ancient terrains of Ganymede and Callisto, each moon offers a unique window into the wonders of our celestial neighborhood.
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of Jupiter's moons, we are on the cusp of unlocking invaluable knowledge about the origins of life, the geological processes that shape celestial bodies, and the intricate interplay between planets and their satellites. With every new discovery, we edge closer to a more profound understanding of our place in the vast cosmos.